Fungal infections of the skin and soft tissue can be uncomfortable and sometimes difficult to treat. While Cephalexin 500Mg is typically used for bacterial infections, understanding how to manage fungal infections is equally important. Here are six key aspects of fungal infections and their treatment.
1. Common Types of Fungal Infections
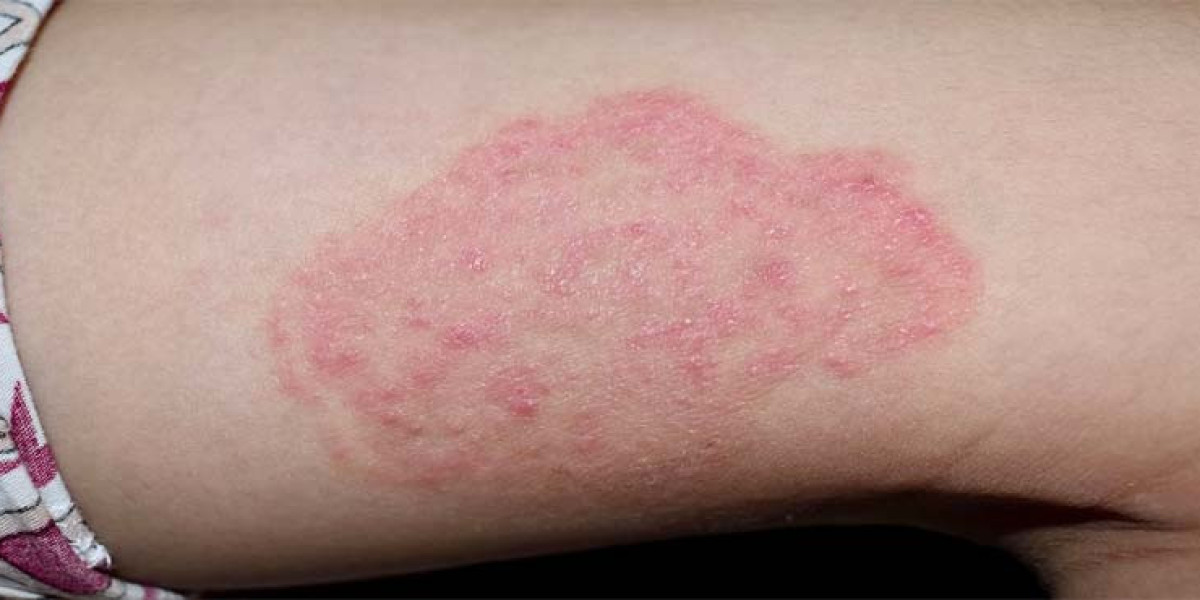
Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, including the skin and soft tissues. Common types include athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, and yeast infections. These infections are caused by different types of fungi, such as dermatophytes and yeast, which thrive in warm, moist environments.
2. Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Symptoms of fungal infections vary depending on the type and location of the infection. Common signs include itching, redness, swelling, and the appearance of a rash or lesions. In some cases, the skin may become scaly or develop blisters. Prompt identification of symptoms is crucial for effective treatment.
3. Causes and Risk Factors
Fungal infections are typically caused by direct contact with the fungus or through spores in the environment. Risk factors include a weakened immune system, poor hygiene, excessive sweating, and prolonged exposure to moist environments. People with diabetes or those taking antibiotics like Cephalexin 500Mg are also at higher risk.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of fungal infections often involves a physical examination and, in some cases, a skin biopsy or culture. Treatment options vary but generally include topical antifungal creams, ointments, and oral medications. Over-the-counter treatments can be effective for mild infections, while prescription-strength medications may be necessary for more severe cases.
5. Home Remedies and Prevention
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help manage fungal infections. Keeping the affected area clean and dry, using antifungal powders, and wearing breathable clothing can prevent the growth of fungi. Natural remedies, such as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, and coconut oil, have antifungal properties and can be used as complementary treatments.
6. When to See a Doctor
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if the infection does not improve with home treatment, if it spreads, or if it is accompanied by severe symptoms like fever or significant pain. In some cases, fungal infections can lead to complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
While Cephalexin 500Mg is not typically used for fungal infections, understanding the nature of these infections and their treatment options is crucial for effective management. Proper hygiene, prompt treatment, and preventive measures can help control and prevent the spread of fungal infections. Always seek professional medical advice for persistent or severe infections to ensure appropriate and effective treatment.